Scams and phishing tactics are continually evolving, but some common techniques are frequently used by cybercriminals to deceive individuals and organizations. Awareness of these tactics is crucial for staying vigilant and avoiding falling victim to scams. Here are some common scams and phishing tactics:
- Email Phishing:
- Spoofed Emails: Cybercriminals create emails that appear to come from legitimate sources, such as banks, government agencies, or popular websites, to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information.
- Deceptive Links: Emails may contain links that, when clicked, lead to fake websites designed to steal login credentials or distribute malware.
- Spear Phishing: This is a targeted form of phishing where attackers customize their approach for specific individuals or organizations. They may use information gathered from social media to create convincing and personalized messages.
- Vishing (Voice Phishing): Scammers use phone calls to impersonate legitimate entities, such as banks or government agencies, and manipulate individuals into providing sensitive information, such as Social Security numbers or financial details.
- Smishing (SMS Phishing): Similar to email phishing, smishing involves sending phishing messages via SMS (text messages). These messages often contain links to malicious websites or ask recipients to reply with sensitive information.
- Social Media Scams:
- Impersonation: Cybercriminals create fake profiles or impersonate real ones to trick individuals into sharing personal information or sending money.
- Fake Contests: Scammers may pose as companies or influencers, claiming that individuals have won a prize or a giveaway. Victims are then asked to provide personal information or pay fees.
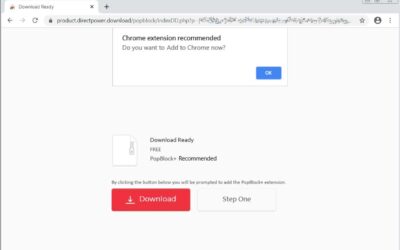
- Tech Support Scams: Individuals receive unsolicited calls or pop-up messages claiming to be from technical support services. The scammers typically allege that the victim’s computer has a virus and request remote access or payment for unnecessary services.
- Online Shopping Scams: Fraudulent websites offer goods or services at prices that seem too good to be true. Victims make payments but never receive the promised items.
- Job Offer Scams: Fake job postings or work-from-home opportunities lure individuals with promises of high-paying jobs. Victims may be asked to pay upfront fees or provide personal information.
- Invoice and Business Email Compromise (BEC): Cybercriminals compromise business email accounts to impersonate executives or employees. They then send fake invoices or request wire transfers, diverting funds to fraudulent accounts.
- Lottery or Prize Scams: Victims receive notifications claiming they have won a lottery or prize. To claim the winnings, they are asked to pay fees or provide personal information.
- Romance Scams: Cybercriminals create fake online profiles on dating websites or social media to establish romantic relationships with victims. They then request money for various reasons, such as a medical emergency or travel expenses.
- IRS or Tax Scams: Scammers impersonate tax authorities, claiming that the victim owes back taxes. They threaten legal action or arrest unless immediate payment is made.
To protect yourself from these scams:
- Be cautious about sharing personal information, especially in response to unsolicited messages.
- Verify the legitimacy of emails, messages, or calls from unfamiliar sources.
- Use strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication where available.
- Keep your software, antivirus, and operating systems up to date.
- Educate yourself and others about common scams and phishing tactics.
If you receive a suspicious communication, it’s wise to independently verify its legitimacy through official channels before taking any action.